In today's world, where green agricultural development and environmental protection are deeply integrated, organic fertilizer production lines have long transcended their simple function as production tools. Their value is widely reflected in multiple key areas, including environmental pollution control, agricultural quality improvement, and economic income increase, becoming an important link connecting ecological protection and industrial upgrading, and injecting strong momentum into sustainable development.
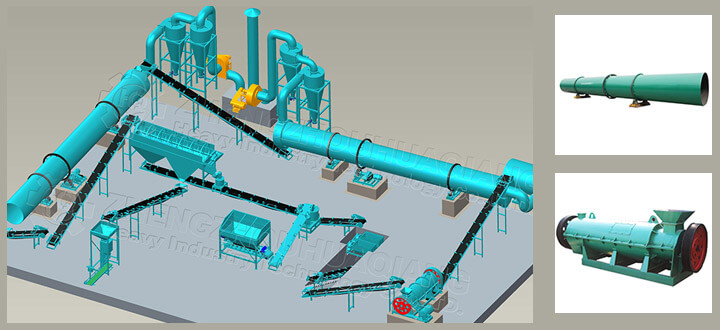
The primary use of organic fertilizer production lines is reflected in the resource utilization of organic waste and environmental pollution control. In the past, waste such as livestock manure, crop straw, and municipal sludge was indiscriminately piled up, polluting soil, water sources, and air, and causing resource waste. Now, production lines, through automated processes such as crushing, mixing, and high-temperature fermentation, transform these "ecological burdens" into high-quality organic fertilizers, turning waste into valuable resources. For example, after treatment by the production line, manure from large-scale farms can completely kill pathogenic bacteria and insect eggs, and exhaust gases are purified before discharge, effectively solving the problem of odor pollution and reducing pollutant emissions, helping to meet environmental standards and solving the problem of waste disposal.
In the field of agricultural production, the use of production lines is a key support for soil improvement and agricultural product quality enhancement. Traditional composting has a long cycle and uneven nutrient distribution, while organic fertilizer production lines can precisely control fermentation parameters, producing organic fertilizers with balanced nutrients and high maturity. This not only replenishes soil organic matter and improves problems such as soil compaction and salinization, but also enhances the soil's water and fertilizer retention capacity. Long-term use can activate soil microbial activity, reduce reliance on chemical fertilizers, make crops taste better and of higher quality, promote the development of organic agriculture, and meet consumer demand for green agricultural products.
Its use is also reflected in improving quality and efficiency and increasing economic income, promoting high-quality industrial development. The production line realizes large-scale and automated production of organic fertilizers. The PLC control system can adjust production parameters in real time, significantly shortening the fermentation cycle, reducing labor costs, and improving production efficiency. At the same time, granular organic fertilizer is easy to store and transport, making it more competitive in the market. It can create additional income for farms and cooperatives, and also drive employment for farmers, contributing to rural revitalization. In addition, national policy subsidies for organic fertilizer production further reduce production costs, making the benefits of using production lines even more prominent.
From environmental protection and pollution control to agricultural quality improvement, and from resource recycling to economic income generation, the use of organic fertilizer production lines spans multiple dimensions of ecology, agriculture, and the economy. It not only embodies the concept of green development and solves multiple development challenges, but also establishes a circular chain of "waste materials—organic fertilizer—high-quality agricultural products," providing a practical solution for sustainable agricultural development and environmental protection. Its value is continuously demonstrated in practice, and its prospects are vast.