According to incomplete statistics, a cow weighing 600 kilograms has a daily fecal output of 20 kilograms, a urine output of 34 kilograms, and a flushing water volume of 500-800 kilograms (head/day) in the cattle farm. Untreated cow dung is piled up and discharged at random, some directly into rivers, lakes, ditches, ponds, some directly piled up outside the pen and beside the road. In rainy days, a large amount of dung water overflows, causing serious pollution to the surrounding environment, roads, land, water and air, resulting in black and smelly water, dirty air, disease spread, endangering the safety of human and livestock drinking water, and increasing the risk of zoonosis, Seriously endangering human and animal health and even life safety, cow manure has seriously restricted the development of the dairy farming industry.
The powdery Organic fertilizer production line has simple process and low input cost, which is suitable for small and medium-sized enterprises and farmers. It only needs to be equipped with: trough fermentation dumper, semi wet material grinder, drum screening machine, automatic quantitative packaging scale, which can meet the production needs.
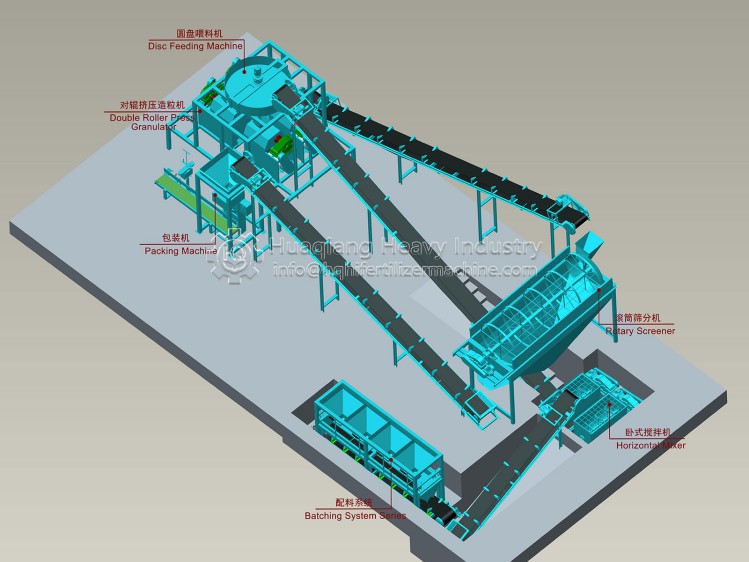
Process flow of powder Organic fertilizer production line:
The whole production process of powdered Organic fertilizer can be simply divided into three processes: pretreatment, one-time fermentation and post-treatment. The process flow of the whole powdery Manure production line specifically includes physical dehydration of fresh crop stalks → crushing of dry raw materials → screening → mixing (bacteria+fresh livestock manure+crushed crop stalks are mixed in proportion) → composting and fermentation → temperature change observation → blowing and turning → moisture control → screening → finished products → packaging → warehousing.
1. Pretreatment stage of powdery Manure: after the compost raw materials are transported to the storage yard and weighed by the scale, they are sent to the mixing and stirring device, mixed with the production and domestic organic wastewater in the plant, added with compound bacteria, and the moisture and carbon nitrogen ratio of the compost are roughly adjusted according to the raw material composition. After mixing, the next process is started. If the Manure raw materials are mixed, the C/N ratio is controlled at 23-28, and the water content of the materials after mixing is controlled at 52% -68%. Raw material stacking requirements: height of meters, width of meters, length of any length, and attention should be paid to a naturally ventilated area.
2. Primary fermentation stage of powdery Manure: the mixed raw materials are fed into the primary fermentation tank with a loader to form a fermentation pile. The fan is used to force ventilation from the bottom of the fermentation tank to the top for oxygen supply. The temperature rises to above 60 degrees, and the pile is turned after 48 hours (but when the temperature exceeds 70 degrees, the pile must be turned immediately). When turning the pile, it must be uniform and thorough. Lower layer materials should be turned into the middle and upper parts of the pile as far as possible to fully mature, Determine the number of times the material is flipped based on its degree of maturity. At the same time, the pile will be flipped for about 2 days and supplemented with water (mainly organic wastewater from production and domestic use) and nutrients. The fermentation temperature will be controlled between 500 ° C and 650 ° C for aerobic fermentation. The fermentation cycle for this project is 8 days, with one tank of raw materials entering and one tank of semi-finished products exiting each day. After the fermented semi-finished products are discharged, they are ready to enter the next process.
3. Post treatment stage of powdery Manure: further screen the finished compost, and treat the undersize according to the water content. After sieving and granulating, the material is sent to a dryer heated by biogas in the biogas digester for drying. After adding medium and trace elements in proportion, it is stirred and mixed to make a finished product, which is then packaged and stored for sale. The screened material is returned to the crushing process for reuse.