The slow-release NPK fertilizer production line is committed to producing high-quality fertilizers that can release nutrients for a long time, and its processing flow involves multiple special links.
In the raw material preparation stage, in addition to conventional nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium raw materials, it is also necessary to prepare additives with slow-release functions, such as high molecular weight polymers, natural minerals, etc. Conduct strict quality testing on all raw materials to ensure compliance with production requirements. According to the precise formula, use high-precision measuring equipment to weigh various raw materials.
After being measured, the raw materials enter the pre-processing stage. Some raw materials may require special treatment, such as activating certain minerals, to improve their compatibility and sustained-release effect with other components. At the same time, some of the raw materials will be crushed to make their particle size more suitable for subsequent processing.
Then proceed to the mixing process. Transport the preprocessed raw materials to a powerful fertilizer mixer and mix thoroughly to ensure even distribution of various components. During the mixing process, appropriate binders can be added to enhance the bonding force between materials and prepare for subsequent granulation.
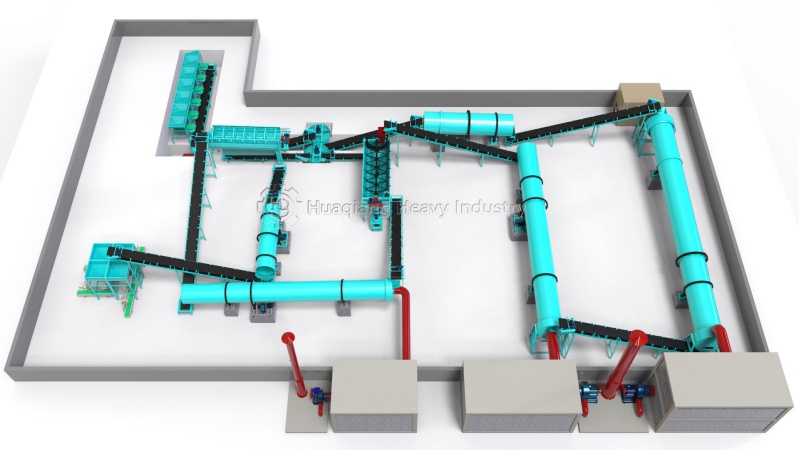
Granulation is a crucial step. Using specialized slow-release granulation equipment, such as fluidized bed granulators or disc granulators combined with special processes. During the granulation process, the slow-release additive is evenly wrapped around the core of the fertilizer particles to form a structure with slow-release function. By adjusting the granulation parameters, control the particle size and the thickness of the slow-release layer.
After granulation is completed, dry it. Use low-temperature drying equipment to avoid high-temperature damage to the slow-release structure. The drying process requires precise control of temperature and time to ensure that the fertilizer particles reach the appropriate moisture content while maintaining stable slow-release performance.
The dried particles enter the cooling stage. By using air cooling equipment to rapidly cool the particles, the hardness and stability of the particles are improved, preventing deformation or damage during subsequent processing.
Next is the screening step. Use a vibrating screen to screen out particles that meet the particle size requirements. Unqualified particles are returned for re granulation.
To further enhance the sustained-release effect, qualified particles are subjected to secondary coating treatment. Using special coating materials to wrap the particles again and enhance the sustained-release function.
Finally, there is the packaging stage. Approved slow-release NPK fertilizers are packaged by an automatic packaging system according to the specified weight. The packaging material should be selected from materials with good moisture and oxygen barrier properties to protect the slow-release performance of fertilizers. Mark the slow-release characteristics, nutrient release cycle, and other information in detail on the packaging bag to complete the entire processing flow.